Synthesis of efficient near-infrared-emitting CuInS2/ZnS quantum dots by inhibiting cation-exchange for bio application†
Abstract
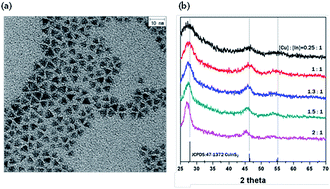
Near-infrared (NIR)-emitting CuInS2(CIS)/ZnS quantum dots (QDs) were synthesized using an off-stoichiometry effect, and the tuned emission wavelength was 850 nm, which is suitable for deep tissue imaging. Due to the unintentional occurrence of cation exchange, however, the emission wavelength of the synthesized CIS core was blue-shifted after ZnS shell coating. In order to inhibit this blue-shift, controlling the synthesis temperature during ZnS shell coating was required, and the selected synthesis temperatures were 180 °C, 210 °C, 230 °C, and 250 °C. The effect of temperature on the emission properties of CIS/ZnS QDs could be related to substitutional diffusion of Zn2+ ions, as expressed by Fick's law. The least blue-shifted emission wavelength was 810 nm and the amount of blue-shift was about 40 nm. Also, at each synthesis temperature, different dynamic behavior of the photoluminescence (PL) peak components was observed when ZnS was coated on the surface of the CIS core. These PL peak components are believed to be defect-related emission of CIS/ZnS QDs, and were analyzed by low-temperature PL. Four PL peak components were observed and the change in each PL peak component could be due to cation exchange. The degree of passivation by the ZnS shell at different synthesis temperatures results in a PL quantum yield (QY) of 26–38%. To evaluate the possibility of applying CIS/ZnS QDs to bio-imaging, an experiment to convert the hydrophobic surface of QDs to a hydrophilic one was carried out using a human serum albumin (HSA)/N-hydroxysuccinimide-functionalized six-arm-branched poly(ethylene glycol)(6-arm PEG-NHS) encapsulation method. The 6-armend PEG-NHS was used as an amphiphilic ligand, and its fluorescence intensity was decreased to 57% of that of the initial QDs after fabrication of the QD-HSA/PEG nanocapsules. The size of the nanocapsules was 140 ± 21.6 nm, measured by SEM and TEM.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...