Structural, optical and magnetic properties of N ion implanted CeO2 thin films
Abstract
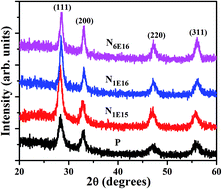
The present study reports the structural, morphological, optical and magnetic properties of N ion implanted CeO2 thin films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering technique. These CeO2 thin films were implanted with N ions having an energy of 80 keV with varying fluencies of 1 × 1015, 1 × 1016 and 6 × 1016 ions per cm2, respectively. X-ray diffraction measurements show that as deposited films had predominantly (111) orientations. There is a significant change in the crystalline nature of these films after implantation compared to pristine film. RBS measurements confirm the presence of N ions in CeO2 thin film with the highest fluence. The closely packed circular shaped nanoparticles were observed through AFM images both in pristine and N ion implanted CeO2 films and these were agglomerated on the surface at a fluence of 6 × 1016 ions per cm2. The crystalline structure and defect related information were evident through Raman spectroscopy. Raman results show that the crystalline structure is maintained even after implantation while the defect related peak is highest for the fluence value of 1 × 1015 ions per cm2 and decreases thereafter. The magnetic measurements show enhanced ferromagnetic ordering in N ion implanted CeO2 films compared to pristine film. The saturation magnetization is highest for the lowest fluence of N ions (1 × 1015 ions per cm2) which decreases with ion fluences. This diverse defect nature of oxygen vacancies (VO) in the N ion implanted CeO2 thin films mediates the ferromagnetic ordering.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...