Investigation of luminescence and structural properties of ZnO nanoparticles, synthesized with different precursors
Abstract
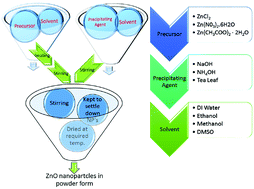
Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) were synthesized by chemical methods using different precursors (zinc chloride, zinc nitrate hexahydrate and zinc acetate) and media (water, ethanol, and methanol). An effort has been made to precisely control the particle size and optical band gap by various methods, while maintaining the crystal structure. The particle sizes of the synthesized ZnO nanoparticles were found to be in the range of 5 nm to 20 nm, by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM). X-ray diffraction (XRD) confirmed the hexagonal crystal structure of all the samples, with a variation in the average crystalline size, in accordance with the TEM studies. Absorption spectra of these nanoparticles exhibit broad peaks in the range of 274 to 376 nm. Optical band gap values of the synthesized ZnO NPs were found to be in the range of 3.2 eV to 3.32 eV. The photoluminescence (PL) spectra show two emission peaks; one at 393–420 nm which corresponds to band gap excitonic emission, and another located at 520–550 nm, due to the presence of defects. Variations in peak positions of the emission spectra are due to changes in the defect densities on the surfaces of the nanoparticles which were synthesized with different precursors. The number of sub peaks obtained from Gaussian peak function fitting of PL spectra shows the possible energy levels, the types of defects present in the samples and also their influence on the optical properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...