Hexamethylphosphoramide as a highly reactive catalyst for the reversible-deactivation radical polymerization of MMA with an in situ formed alkyl iodide initiator†
Abstract
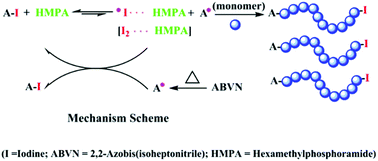
Hexamethylphosphoramide (HMPA) has been found to be a novel and highly efficient organic catalyst for the reversible-deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) of methyl methacrylate (MMA) with an in situ formed alkyl iodide initiator. The polymerization results exhibited typical features of “living”/controlled radical polymerization. The polymerization process efficiently controls the molecular weight and chemical structure of the resultant poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA). Furthermore, the inhibition period was shortened and the polymerization rate was increased upon the addition of HMPA as compared to blank controls. Due to the high reactivity of HMPA, the molecular weight and molecular weight distribution of the resultant PMMA were well controlled at high monomer conversions at mild temperatures (Mw/Mn = 1.12–1.22, 60–70 °C). Notably, high-molecular-weight PMMA with a narrow molecular weight distribution were successfully obtained (Mn up to 104 000, Mw/Mn = 1.34). The living feature of the obtained polymers was confirmed by chain extension and block copolymerization. The mechanism for the controlled polymerization catalyzed by HMPA was also discussed. In brief, HMPA as a catalyst for RDRP with in situ formed alkyl iodide not only could simplify the polymerization process but also would be applicable as a powerful and robust method for well-defined polymers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...