Self-assembly and disassembly of stimuli responsive tadpole-like single chain nanoparticles using a switchable hydrophilic/hydrophobic boronic acid cross-linker†
Abstract
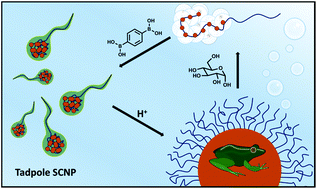
Living systems are driven by molecular machines that are composed of folded polypeptide chains, which are assembled together to form multimeric complexes. Although replicating this type of system is a longstanding goal in polymer science, the complexity the structures impose is synthetically very challenging, and generating synthetic polymers to mimic the process of these assemblies appears to be a more appealing approach. To this end, we report a linear polymer programmable for stepwise folding and assembly to higher order structures. To achieve this, a diblock copolymer composed of 4-acryloylmorpholine and glycerol acrylate was synthesised with high precision via reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer polymerisation (Đ < 1.22). Both intramolecular folding and intermolecular assembly were driven by a pH responsive cross-linker, benzene-1,4-diboronic acid. The resulting intramolecular folded single chain nanoparticles were well defined (Đ < 1.16) and successfully assembled into a multimeric structure (Dh = 245 nm) at neutral pH with no chain entanglement. The assembled multimer was observed with a spherical morphology as confirmed by TEM and AFM. These structures were capable of unfolding and disassembling either at low pH or in the presence of sugar. This work offers a new perspective for the generation of adaptive smart materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...