Bioinspired polydopamine-induced assembly of ultrafine Fe(OH)3 nanoparticles on halloysite toward highly efficient fire retardancy of epoxy resin via an action of interfacial catalysis†
Abstract
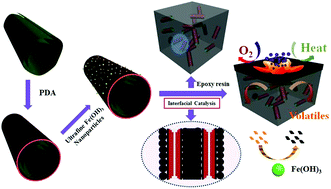
Inspired by the core–sheath-dot structure of corncobs, halloysite nanotubes (HNT) were sequentially functionalized with a biomimetic polydopamine (PDA) nanocoating and ultrafine Fe(OH)3 nanoparticles to prepare hierarchical HNT@PDA@Fe(OH)3, with the aim of endowing epoxy resin (EP) with improved fire retardancy, thermal stability and mechanical properties. The target product was characterized via Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). As a result, in a study of thermal degradation a nanocomposite of EP with HNT@PDA@Fe(OH)3 generated a notably higher yield of char and exhibited a lower maximum degradation rate than its counterparts. An investigation of fire retardancy revealed that EP/5HNT@PDA@Fe(OH)3 possessed an LOI value of 33.9% and a UL-94 vertical burning rating of V-1, which represent significant enhancements in comparison with neat EP (LOI = 24.1%, no rating). In a cone calorimeter test (CCT) at 50 kW m−2, EP/5HNT@PDA@Fe(OH)3 gave rise to a 41% reduction in peak heat release rate (pHRR) relative to that of EP/5HNT. A TG-FTIR test disclosed that HNT@PDA@Fe(OH)3 notably decreased the evolution of volatiles (CO, aliphatic compounds, aromatic compounds, and carbonyl compounds), which resulted in less flammable gases. Variable-temperature FTIR, Raman spectra and SEM observations revealed that char with a more compact and continuous structure was obtained with HNT@PDA@Fe(OH)3. In addition, the tensile strength and modulus were remarkably enhanced, accompanied by an increase in the dynamic storage modulus (E′). Finally, a probable mechanism was proposed to account for the improved fire retardancy, which involved catalytic charring behavior at the interface (determined by TG-GC-MS) and intensive protection by char.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...