Solvent-free electrospinning: opportunities and challenges
Abstract
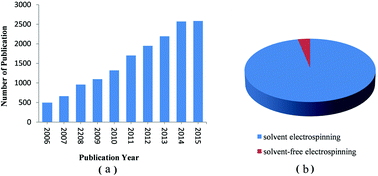
Electrospinning (e-spinning) has attracted tremendous attention because this technology provides a simple and versatile method for fabricating ultrafine fibers from a rich variety of materials including polymers, composites, and ceramics. However, an overwhelming majority of publications focus on solution e-spinning that processes polymer solutions into continuous ultrafine fibers with a low precursor utilization (usually less than 20 wt%). Only a few groups have paid attention to solvent-free e-spinning such as melt e-spinning to avoid solvent emission into air and achieve highly efficient utilization of precursors (e.g., more than 90 wt%). More importantly, solvent-free electrospun (e-spun) fibers without any solvent residue provide opportunities in some interesting fields such as tissue engineering and wound dressings. Herein, we aim to highlight recent research studies and future trends of solvent-free e-spinning such as melt e-spinning, supercritical CO2-assisted e-spinning, anion-curing e-spinning, UV-curing e-spinning and thermocuring e-spinning, which may be further developed into efficient, controllable and ecofriendly processes for the generation of ultrafine fibers. Here, solvent-free e-spinning is defined as an e-spinning technique which never uses a conventional solvent, or nearly all of the precursor solution spins into ultrathin fibers so that only a few precursors enter air via evaporation, and the utilization ratio of precursor can reach more than 90%. Compared to solution e-spinning, solvent-free e-spinning may open the door to new horizons in modeling e-spinning without any risk of solvent residue in fibers, solvent evaporation into air and high cost of solvent recycling, and offers potentially broad applications in biomedicine, tissue engineering, textiles, filtration and other fields. Finally, some challenges in solvent-free e-spinning are discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...