Lipid remodelling in human melanoma cells in response to UVA exposure
Abstract
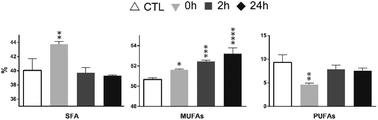
Extensive exposure to UVA is thought to increase the risk of malignancy and the progression of melanoma, the most serious type of skin cancer. It is well known that alterations in lipid metabolism represent an early event in carcinogenesis, but the impact of UVA exposure on the lipid composition of cancer cells is still largely unknown. In this study we aimed at investigating lipid remodeling in human melanoma cells in response to UVA exposure. After UVA irradiation, lipid extracts were either immediately collected from SK-MEL-28 cells or collected after a recovery period of 2 h or 24 h. The lipid profiles for each event were determined by liquid chromatography or gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. UVA exposure led to major alterations in both fatty acids (FA) and phospholipid profiles. An increase of monounsaturated FA (MUFA) and FA18:0, as well as a decrease of FA16:0, were observed 24 h after irradiation. Moreover, phosphatidylcholine (PC) decreased and phosphatidylinositol (PI) increased after UVA exposure. Molecular alterations in the PC, lysoPC, PI, phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), ether-linked PE and phosphatidylglycerol (PG) profiles were also observed. The absence of cleaved caspase-3 after 2 h and 24 h of re-incubation is correlated with impairment of apoptosis. Overall, these data showed changes in membrane lipids, which may be associated with lipogenesis after UVA exposure which, in turn, is usually a determinant for cell survival.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...