Isoindoline nitroxide-labeled porphyrins as potential fluorescence-suppressed spin probes†
Abstract
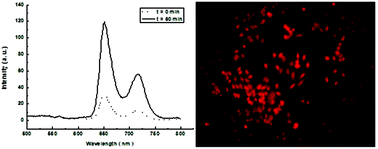
A series of isoindoline nitroxide-labeled porphyrins were synthesized by the reaction of 5-phenyldipyrromethane and 5-(4′-carboethoxy-methyleneoxyphenyl)dipyrromethane with 5-formyl-1,1,3,3-tetramethylisoindolin-2-yloxyl (FTMIO) using the Lindsey method. The corresponding water-soluble spin-labeled porphyrins were also prepared. Subsequently, these compounds were characterized and their in vitro properties were evaluated. The electrochemical assay demonstrated that these isoindoline nitroxide-labeled porphyrins had similar electrochemical and redox properties to 5-carboxy-1,1,3,3-tetramethylisoindolin-2-yloxyl (CTMIO). The electron paramagnetic resonance test showed that these porphyrins exhibited hyperfine splittings and characteristic spectra of CTMIO with typical nitroxide g-values and nitrogen isotropic hyperfine coupling constants. The in vitro cytotoxicity assay indicated that these porphyrins possessed low cytotoxicity to human renal tubular epithelial 293T cells (normal cells) and human hepatoma HepG2 cells (tumor cells). Fluorescence spectroscopy revealed that free base isoindoline nitroxide-labeled porphyrins exhibited fluorescence suppression characteristic of nitroxide–fluorophore systems. In vitro fluorescene imaging demonstrated that the reduced isoindoline nitroxide-labeled porphyrins eliminated fluorescence suppression and displayed strong red fluorescence imaging in HepG2 cells. Thus these isoindoline nitroxide-labeled porphyrins may be considered potentially as biological spin probes for fluorescence imaging and EPR spectroscopy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...