Nano- and micromotors for cleaning polluted waters: focused review on pollutant removal mechanisms
Abstract
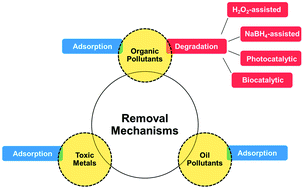
Nano- and micromotors are machines designed to self-propel and—in the process of propelling themselves—perform specialized tasks like cleaning polluted waters. These motors offer distinct advantages over conventionally static decontamination methods, owing to their ability to move around and self-mix—which heightens the interaction between their active sites and target pollutants—thus improving their speed and efficiency, which could potentially decrease treatment times and costs. In the last decade, considerable research efforts have been expended on exploring various mechanisms by which these motors can self-propel and remove pollutants, proving that the removal of oil droplets, heavy metals, and organic compounds using these synthetic motors is possible. This review highlights recent progress in the design of these nano- and micromotors for cleaning polluted waters, and gives an overview of their structure, fabrication, and propulsion methods, with a special focus on the mechanisms by which they remove pollutants—namely, either by adsorption or by degradation. A fundamental understanding of these removal mechanisms, with their attendant advantages and disadvantages, can help researchers fine-tune motor design in the future so that technical issues can be resolved before they are scaled-up for a wide variety of environmental applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...