A one step method for the functional and property modification of DOPA based nanocoatings†
Abstract
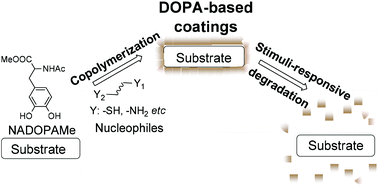
Biomimetic poly(catecholamine) coatings have gained much attention in recent years due to their versatility as functional materials. Despite this, only limited methods are available to modify the function and property of poly(catecholamine) coatings, primarily through post-modification methods. Our approach reported herein provides a simple approach to the fabrication of novel functionalized poly(catecholamine) coatings. The strategy employs the copolymerization of N-Ac-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine methyl ester (NADOPAMe) with nucleophilic additives, giving rise to nano-coatings on various surfaces including plastic, metal, glass and polymers. With the appropriate choice of nucleophilic additives, coatings with desired properties can be achieved. This is demonstrated through the fabrication of a redox responsive coating based on NADOPAMe with cysteamine as additive, which shows a concentration-dependent glutathione (GSH) responsive behavior. The ability to utilize this as a controlled release system is also demonstrated.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...