Photosensitizer localization in amphiphilic block copolymers controls photodynamic therapy efficacy†
Abstract
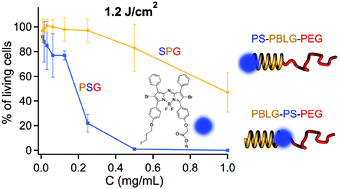
Localization of the photosensitizer conjugation site in amphiphilic block copolymers is shown to have a great impact on photodynamic therapy efficiency. To this end, an asymmetric multifunctional derivative of the azadipyrromethene boron difluoride chelate (aza-BODIPY) was synthesized and inserted at specific locations in polypeptide-based rod-coil amphiphilic block copolymers. A study of the photophysical properties of the vesicle nanocarriers, obtained by self-assembly of these copolymers, as well as in vitro tests on two cancer cell lines were performed. This study aims at providing guidelines for the optimization of the synthetic design of therapeutic nanomedicines with minimal amounts of photosensitive molecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...