NIR-emissive PEG-b-TCL micelles for breast tumor imaging and minimally invasive pharmacokinetic analysis†
Abstract
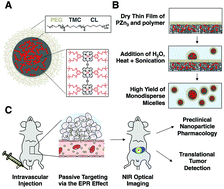
Motivated by the goal of developing a fully biodegradable optical contrast agent with translational clinical potential, a nanoparticle delivery vehicle was generated from the self-assembly of poly(ethylene-glycol)-block-poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-caprolactone) (PEG-b-TCL) copolymers. Cryogenic transmission electron microscopy verified that PEG-b-TCL-based micelles were formed at low solution temperatures (∼38 °C). Detailed spectroscopic experiments validated facile loading of large quantities of the high emission dipole strength, tris(porphyrin)-based fluorophore PZn3 within their cores, and the micelles displayed negligible in vitro and in vivo toxicities in model systems. The pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of PZn3-loaded PEG-b-TCL-based micelles injected intravenously were determined via ex vivo near-infrared (NIR) imaging of PZn3 emission in microcapillary tubes containing minute quantities of blood, to establish a novel method for minimally invasive pharmacokinetic monitoring. The in vivo circulatory half-life of the PEG-b-TCL-based micelles was found to be ∼19.6 h. Additionally, longitudinal in vivo imaging of orthotopically transplanted breast tumors enabled determination of micelle biodistribution that correlated to ex vivo imaging results, demonstrating accumulation predominantly within the tumors and livers of mice. The PEG-b-TCL-based micelles quickly extravasated within 4T1 orthotopic mammary carcinomas, exhibiting peak accumulation at ∼48 h following intravenous tail-vein injection. In summary, PEG-b-TCL-based micelles demonstrated favorable characteristics for further development as in vivo optical contrast agents for minimally invasive imaging of breast tumors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...