Polylactic acid nano- and microchamber arrays for encapsulation of small hydrophilic molecules featuring drug release via high intensity focused ultrasound†
Abstract
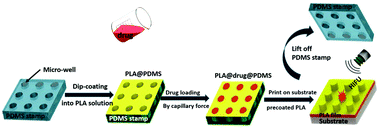
Long term encapsulation combined with spatiotemporal release for a precisely defined quantity of small hydrophilic molecules on demand remains a challenge in various fields ranging from medical drug delivery, controlled release of catalysts to industrial anti-corrosion systems. Free-standing individually sealed polylactic acid (PLA) nano- and microchamber arrays were produced by one-step dip-coating a PDMS stamp into PLA solution for 5 s followed by drying under ambient conditions. The wall thickness of these hydrophobic nano–microchambers is tunable from 150 nm to 7 μm by varying the PLA solution concentration. Furthermore, small hydrophilic molecules were successfully in situ precipitated within individual microchambers in the course of solvent evaporation after sonicating the PLA@PDMS stamp to remove air-bubbles and to load the active substance containing solvent. The cargo capacity of single chambers was determined to be in the range of several picograms, while it amounts to several micrograms per cm2. Two different methods for sealing chambers were compared: microcontact printing versus dip-coating whereby microcontact printing onto a flat PLA sheet allows for entrapment of micro-air-bubbles enabling microchambers with both ultrasound responsiveness and reduced permeability. Cargo release triggered by external high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) stimuli is demonstrated by experiment and compared with numerical simulations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...