Redox and pH dual sensitive bone targeting nanoparticles to treat breast cancer bone metastases and inhibit bone resorption†
Abstract
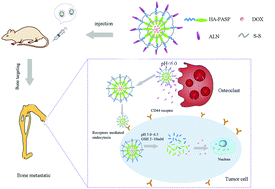
Bone is an especially prone metastatic site for breast cancer, and to block the vicious cycle between bone resorption and tumor growth is an important strategy for the treatment of breast cancer bone metastasis. In this paper, pH- and redox-sensitive as well as breast cancer bone metastasis-targeting nanoparticles (DOX@ALN-(HA-PASP)CL) were prepared, and also their anti-tumor activity and anti-bone resorption effect were investigated in detail. The in vitro experimental results indicated that DOX released from DOX@ALN-(HA-PASP)CL exhibited a GSH-, DTT- and pH-dependent manner. Moreover, in an in vitro 3D breast cancer bone metastasis model, DOX@ALN-(HA-PASP)CL decreased bone resorption through inhibiting the proliferation of human breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231 cells) and reducing the activity of osteoclasts. The in vivo experimental results indicated that a large amount of DOX was delivered to a breast cancer bone metastasis site after tumor-bearing mice were treated with DOX@ALN-(HA-PASP)CL; meanwhile, DOX@ALN-(HA-PASP)CL significantly decreased the tumor volume and bone resorption in tumor-bearing mice without causing obvious systemic toxicity. In conclusion, the in vitro and in vivo experimental results indicate that DOX@ALN-(HA-PASP)CL has great potential in the treatment of breast cancer bone metastasis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...