An approach to high open-circuit voltage polymer solar cells via alcohol/water-soluble cathode interlayers based on anthrathiadiazole derivatives†
Abstract
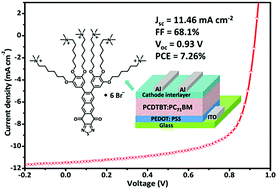
Two small molecular cathode interlayer (CIL) materials with pyridinium ion or quaternary ammonium ion terminated 1,2,3-trihexyloxybenzene as pendant polar groups and anthrathiadiazole-4,11-dione (ATD) as a conjugated backbone, namely PBATD and TBATD, were synthesized for PCDTBT:PC71BM (PCDTBT:poly[poly[N-9′-heptadecanyl-2,7-carbazole-alt-5,5-(4′,7′-di-2-thienyl-2′,1′,3′-benzothiadiazole)]]; PC71BM:[6,6]-phenyl C71-butyric acid methyl ester) based polymer solar cells (PSCs). A dramatic improvement in the device performance was observed when the CILs were inserted between the active layer and the Al electrode. Especially, the device modified by quaternary ammonium ion terminated TBATD exhibits a power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 7.26%, which was 1.4 times that of the device with bare Al as the cathode, due to the simultaneously enhanced open-circuit voltage (Voc), short-circuit current density (Jsc) and fill factor (FF). Importantly, the Voc (0.93 V) achieved for the TBATD modified device was among the top values that used the same kind of active layer in conventional single-junction PSCs so far. It demonstrated that the CILs presented in this study may be a promising candidate for applications in high performance PSCs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...