Oxidation route dependent proton conductivities of oxidized fullerenes†
Abstract
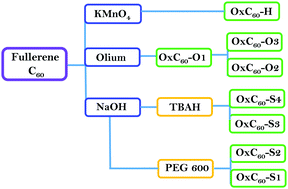
We reported the proton conductivities of a series of oxidized fullerenes (fullerenols) having varied polarity and hydrophilicity. The samples were generated from the oxidation of fullerenes by using different oxidation techniques and oxidizing agents. XPS, IR and TGA data confirmed the successful oxidation of fullerenes. Electrochemical impedance showed that fullerenols can support proton conductivity. At room temperature and 90% RH, a maximum proton conductivity of 1.4 × 10−2 S cm−1 was observed in fullerenols obtained from the oxidation of fullerene (C60) by caustic soda. We expect the use of fullerenols as solid electrolytes in fuel cells, sensors, chemical filters and so on.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...