New metal-free catalytic degradation systems with carbon dots for thymol blue†
Abstract
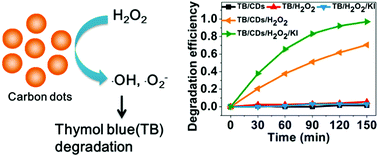
New metal-free catalytic systems with carbon dots (CDs) have been presented for the degradation of thymol blue at room temperature. It was found that degradation efficiency was influenced by the pH value, the concentration of H2O2 and the addition of KI. The degradation mechanisms of catalytic systems were studied by means of electron spin resonance and a free radical quenching technique. The results show that HO˙ and ˙O2− originating from the decomposition of H2O2 in the presence of CDs contribute to the degradation of the dyes. The most important merits of the catalytic system are high degradation efficiency of thymol blue in a near-neutral solution and avoiding secondary pollution from metal ions, which make them environmentally-friendly systems for the treatment of pollutants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...