Synthesis and characterization of multifunctional gold and silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Naregamia alata and their applications in the catalysis and control of mastitis
Abstract
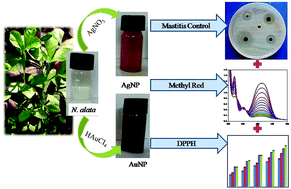
Phytoreduced nanoparticles have multi-functionalities due to their sustainable origin and biocompatible nature. Herein, we report the synthesis and characterization of silver and gold nanoparticles using leaf extract from the herb Naregamia alata. Microwave radiation from a domestic microwave oven, a non-classical source of energy, is used to perform the reduction of the metal ion precursors. The spherical silver nanoparticles have an average diameter of 18.05 ± 4.73 nm, and the poly-shaped gold nanoparticles exhibit an average size of 27.92 ± 9.19 nm. The X-ray powder diffraction patterns indicate different crystal planes, namely the (111), (200), (220) and (311) planes of fcc nanosilver and nanogold. The actions of six major mastitis pathogens are inhibited by the antimicrobial power of the silver and gold nanoparticles. Colored pollutants from the paper, printing and textile industries such as eosin Y and methyl red are degraded without light irradiation using the catalytic power of the synthesized noble metal nanoparticles. Furthermore, the reduction of the organic compound 4-nitrophenol by NaBH4 in the presence of the nanocatalysts increases the laboratory value of the present study.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...