A graphene quantum dot-assisted morin–KMnO4 chemiluminescence system for the precise recognition of cypermethrin†
Abstract
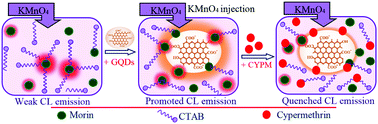
A novel and efficient chemiluminescence (CL) probe was developed based on the sensitizing effect of graphene quantum dots (GQDs) on the morin–KMnO4 CL reaction for cypermethrin (CYPM). GQDs were prepared using an economic and green procedure, and characterized with the help of their distinctive emission and absorption patterns. Advanced morphological and structural investigations of the GQDs were conducted using X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis. The synthesized GQDs showed a remarkable promoting influence on the CL emission of the morin–KMnO4 reaction in the presence of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), offering a powerful and efficient new CL system. The mechanism of the sensitized CL system was described based on the electron transfer processes. In addition, CYPM, as a potent pollutant, could linearly suppress the emission of the KMnO4–morin–CTAB–GQD CL system. This turned the introduced CL system into a susceptible chemosensor for CYPM. Under the selected operating conditions, a linear relation of the CL response was attained over the CYPM concentration range of 0.3–22.0 mg L−1 with a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.08 mg L−1. The proposed method showed good features for the determination of CYPM and was satisfactorily employed for CYPM evaluation in real environmental water samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...