Aqueous synthesis of dual-targeting Gd-doped CuInS2/ZnS quantum dots for cancer-specific bi-modal imaging†
Abstract
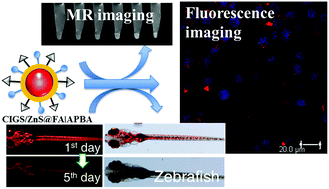
Dual targeting towards cellular receptors specific to tumors is an important approach for cancer diagnosis. In this work, we demonstrated the aqueous synthesis of Gd3+-doped CuInS2/ZnS (CIGS/ZnS) quaternary quantum dots (q-dots), which combine the functions of fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging, via a microwave method. To enhance the tumor-targeting ability, 3-aminophenyl-boronic acid (APBA) and folic acid (FA) moieties were conjugated with the CIGS/ZnS q-dots, and act as dual-targeting ligands to generate CIGS/ZnS@FA|APBA q-dots. In vitro fluorescence imaging and cellular internalization of such q-dots were scrutinized with confocal microscopy, as well as magnetic resonance imaging, which revealed specifically targeted in vitro delivery into HeLa cells containing abundant sialic acid and overexpression of folate receptors on the cell surfaces. As compared to CdTe quantum dots, the formed CIGS/ZnS@FA|APBA q-dots displayed lower in vitro cytotoxicity for both HeLa and HepG2 cells according to the MTT assay. The results also showed that these q-dots neither induce any noticeable abnormalities, nor affect the survival or hatching rate in the embryonic and larval development of zebrafish. More importantly, fluorescence imaging revealed that CIGS/ZnS q-dots at concentrations up to 1000 μg mL−1 were excreted from the zebrafish without a significant effect on growth.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...