Enhanced photocatalytic activity and chemical sensor development based on ternary B2O3·Zn6Al2O9·ZnO nanomaterials for environmental safety†
Abstract
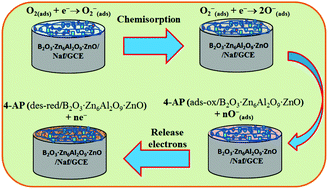
The synthesis of ternary B2O3·Zn6Al2O9·ZnO nanomaterials by a simple co-precipitation method and their potential application as an efficient photocatalyst and chemical sensor has been reported. The synthesized nanomaterial was studied by XRD, SEM, EDS mapping, photoluminescence (PL), FTIR, and UV-visible spectroscopy. This nanocomposite exhibits enhanced efficiency in photo-catalysis in Methyl Violet 6b (MV) dye degradation. It displays an efficiency of 97.24% under visible light and 78.98% under UV light at pH 9. Moreover, it loses only 2.61% efficiency over three cycles of reuse. What’s more, in the presence of H2O2, it can degrade over 98% of the dye within just 1 hour. The PL and PLE properties were also reported with a change in excitation energy and calcination temperature. The PLE shows three equidistant peaks with 20 nm intervals. For potential chemical sensor development, the B2O3·Zn6Al2O9·ZnO nanomaterial was deposited on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) to produce a sensor with a fast and selective response towards 4-aminophenol (4-AP) in phosphate buffer. The sensor also exhibits good sensitivity and long-term stability, and enhanced electrochemical responses. The calibration plot is linear over the 0.1 nM to 0.01 M 4-AP concentration range. The sensitivity and detection limit are calculated from the slope of the calibration plot to be 0.506329 μA cm−2 nM−1 and 0.019 nM (signal-to-noise ratio, at a SNR of 3), respectively. The synthesized ternary B2O3·Zn6Al2O9·ZnO nanomaterials have great potential to be used in the future development of promising efficient photocatalysts and sensitive chemical sensors for the detection and/or degradation of hazardous and carcinogenic toxic commercial dyes and phenolic compounds for improved safety in the environmental and health care fields.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...