The first electrochemical and surface analysis of 2-aminobenzimidazole as a corrosion inhibitor for copper in chloride solution
Abstract
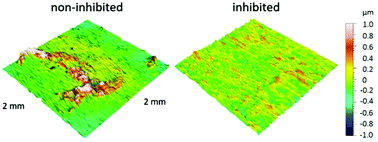
For the first time, 2-aminobenzimidazole (2-ABI) was tested as a corrosion inhibitor for copper in 3 wt% NaCl solution at 25 °C using cyclic voltammetry (CV), chronopotentiometry, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and potentiodynamic curve (PD) techniques. The EIS measurements indicated that the corrosion of Cu in the presence of 2-ABI followed kinetic- and diffusion-controlled processes. After 100 h of immersion, the potentiodynamic curves showed that 2-ABI acts as a mixed-type inhibitor, with a predominant action on the anodic corrosion reaction. ATR-FTIR confirmed the adsorption of 2-ABI on the Cu surface, which resulted in increased hydrophobicity of the copper surface and reduced its surface roughness.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...