Theoretical study of azido gauche effect and its origin†
Abstract
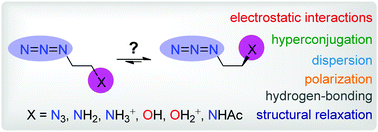
The strength of the azido gauche effect in 1,2-diazidoethane, N-(2-azidoethyl)ethanamide, (protonated) 2-azidoethanamine and (protonated) 2-azidoethanol and its origin were theoretically studied at the MP2/6-311++G(d,p) level of theory. The results show that the azido gauche effect in the amine and alcohol can exert a control over the molecular conformation to a similar extent as the fluorine gauche effect, but to a greater extent in the charged species, amide and vicinal diazido fragment. A quantitative partitioning of isomerization energy into contributions from electrostatic, orbital, dispersion and Pauli interactions and energy consumed in structural changes revealed that electrostatic forces play an important role in the stabilization of the gauche isomer in the two charged species and alcohol. Electrostatic and dispersion interactions are the main contributors to the gauche effect in the amide, whereas dispersion and orbital interactions can be considered to be the two most important stabilizing factors of the gauche form in the vicinal diazido fragment. The interplay of all three stabilizing interactions determines the gauche preference in the amine. Stereoelectronic effects, which are involved in orbital interactions, contribute to the gauche effect in all the molecules except the 2-azidoethylammonium ion and protonated 2-azidoethanol. Hydrogen-bonding interactions were found only in the protonated alcohol.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...