Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B dye under sunlight irradiation of porous titanosilicate (TS)/bismuth vanadate (BiVO4) nanocomposite hybrid catalyst†
Abstract
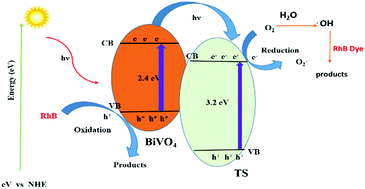
Novel mesoporous titanosilicate/bismuth vanadate (BVTS) inorganic hetero-structures were successfully synthesized under mild conditions. The synthesized mesoporous BVTS hetero-structures were characterized by various analytical techniques for structural and chemical properties. We confirmed from TEM results that a good heterojunction formed between titanosilicate and bismuth vanadate. More significantly, the BVTS hetero-structures exhibited enhanced photocatalytic activity in the degradation of Rhodamine B dye (RhB) under sunlight irradiation. The optimum photocatalytic activity of BVTS 1 under visible light is almost 3.5 and 6.5-fold higher than pure titanosilicate (TS) and pure bismuth vanadate (BVO), respectively. These composites and their photocatalytic Rhodamine-B dye degradation under sun light irradiation is reported for the first time. The popularity of fabrication of heterojunction structures is an inevitable trend. A RhB solution (100 mL, 10−5 M) was degraded in 60 min using the BVTS nanocomposites photocatalyst with visible light irradiation. The BVTS nanocomposites responded well and thus remarkably enhanced photocatalytic efficiency.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...