Phenolic compound-mediated single-step fabrication of copper oxide nanoparticles for elucidating their influence on anti-bacterial and catalytic activity
Abstract
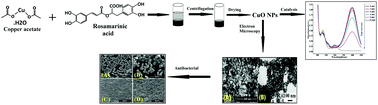
A single-step synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) from a phenolic compound (rosmarinic acid) at ambient temperature was developed in this study. The physico-chemical properties of the synthesized particles were characterized by different instruments (UV-visible; ultra-violet spectroscopy, XRD; X-ray diffraction, FTIR; Fourier transformed infrared resonance, FESEM; field emission scanning electron microscope equipped with EDS; energy dispersive spectroscopy and TEM; transmission electron microscope), which revealed the good crystallinity with homogeneous distribution (30 ± 5 nm) of CuO NPs on the surface. The applicability of the nanoparticles as an anti-bacterial agent against Gram-negative (E. coli) and Gram-positive (S. aureus) bacterial strain was determined by bactericidal kinetics study. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) values as determined by a batch culture process that exhibited a considerably low amount of copper content are capable of enhancing the anti-microbial efficacy. The cyto-compatibility of the CuO NPs was investigated by cell viability (MTT) and proliferation of mammalian fibroblast cell line experiments. The underlying mechanisms behind the anti-microbial activity and cell death were also studied by inner membrane permeabilization assay (β-galactosidase assay), intracellular ROS measurement, fluorescence images and cell wall degradation by FESEM. Significant photocatalytic activity of CuO NPs was observed through the degradation of methylene blue (MB) and para-nitrophenol (PNP) under visible light exposure conditions. The phenolic compound-assisted CuO NPs have the advantages of being environmentally benign with a beneficial and single-step synthesis approach that can be further used for various biomedical and waste water treatment purposes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...