Fe3O4@PVIM@Zn(ii) magnetic microspheres for luteolin recognition via combined reflux-precipitation polymerization and metal-ion affinity strategy†
Abstract
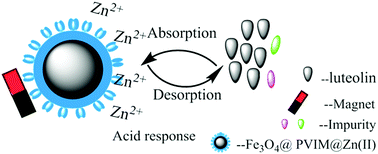
Magnetic microspheres (Fe3O4@PVIM@Zn(II)) composed of a high magnetic-response Fe3O4 core and a Zn(II)-immobilized cross-linked polyvinyl imidazole (PVIM) shell via reflux-precipitation polymerization and metal-ion affinity strategy were fabricated. Integrating the advantages of specific uptake and fast separation, Fe3O4@PVIM@Zn(II) was adopted as an ideal pathway for luteolin (LTL) recognition. As-prepared Fe3O4@PVIM@Zn(II) possessed core–shell structure, uniform size (200 nm), high magnetic responsiveness (32.6 emu g−1), and a very easy synthesis process. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) suggested a strong interaction between the nitrogen heterocyclic ring of PVIM and Zn(II), which produced abundant binding sites for LTL. The batch mode experiments can be well described by pseudo-first-order kinetic models and a Langmuir isotherm. A rapid binding equilibrium (within 45 min) and large monolayer adsorption capacity (23.92 mg g−1) at 298 K were also observed. In addition, Fe3O4@PVIM@Zn(II) displayed remarkable selectivity to LTL; the purification process using Fe3O4@PVIM@Zn(II) can make purified LTL from approximately 85% to 94.26%. The antibacterial activity of purified LTL was outstanding by means of a Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC29213) resistance experiment. Considering its multiple merits, Fe3O4@PVIM@Zn(II) exhibited great potential for specific binding with natural products, such as flavonoids.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...