Application of graphene quantum dots functionalized with thymine and thymine-appended zinc phthalocyanine as novel photoluminescent nanoprobes†
Abstract
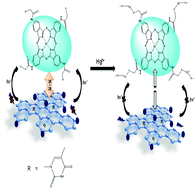
Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) and zinc phthalocyanine (ZnPc) were separately modified with thymine to obtain thymine-functionalized GQDs (T-GQDs) and ZnPc (T-ZnPc). T-GQDs and nanoconjugates of T-ZnPc with pristine GQDs (represented as pristine GQDs–T-ZnPc) or T-GQDs (represented as T-GQDs–T-ZnPc) were employed as fluorescent probes for the detection of mercury(II) ions (Hg2+). The as-synthesized T-GQDs alone demonstrated a highly sensitive and selective fluorescence “turn-OFF” process for Hg2+ detection due to the specific interaction between the thymine functionality on the T-GQDs with Hg2+. On the other hand, the fluorescence of pristine GQDs and T-GQDs was quenched (“turn-OFF”) upon coordination with T-ZnPc. However, the fluorescence emission was selectively restored (“turn-ON” process) in the presence of Hg2+ resulting in the sensitive detection of Hg2+ in the nanomolar concentration range (limit of detection = 0.05 nM, for the pristine GQDs–T-ZnPc probe). The probe containing pristine GQDs and the T-ZnPc complex demonstrated a higher specific and sensitive recognition of Hg2+ as compared to the T-GQDs alone or T-GQDs–T-ZnPc probes which are ascribed to the fluorescence “turn-ON” process of the former. Screening of different metal ions and counter ions proved that the probes are specifically suited for Hg2+ detection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...