Solution-phase and solid-phase sequential, selective modification of side chains in KDYWEC and KDYWE as models for usage in single-molecule protein sequencing†
Abstract
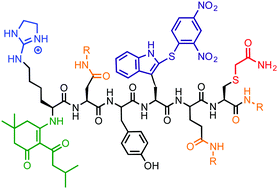
Single-molecule protein sequencing is regarded as a promising new method in the field of proteomics. It potentially offers orders of magnitude improvements in sensitivity and throughput for protein detection when compared to mass spectrometry. However, the development of such a technology faces significant barriers, especially in the need to chemically derivatize specific amino-acid types with unique labels. For example, fluorescent dyes would be suitable for single-molecule microscopy or nanopore-based sequencing. These emerging single-molecule protein-sequencing technologies suggests a need to develop an amino acid side chain-selective modification scheme that could target several side chains of interest. Current work for modifying residues focuses mainly on one or two side chains. The need to label many side chains, as recent computational modeling suggests, is required for high protein, sequencing coverage of the human proteome. Herein, we report our strategy for modifying two model peptides KYDWEC and KDYWE containing the most reactive residues, using highly optimized mass labels in a sequential and selective fashion both using solution-phase and solid-phase chemistries, respectively. This will serve as a step towards a modification scheme appropriate for single-molecule studies.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...