Polyureas derived from CO2 and diamines: highly efficient catalysts for C–H arylation of benzene†
Abstract
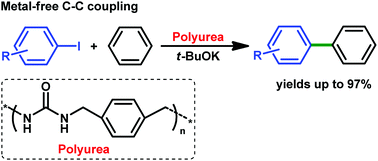
Polyureas derived from CO2 and diamines were effective for C–H arylation of benzene in the presence of t-BuOK, producing biaryl products with various substituents in high yields up to 97%. Dual-activation of K+ and t-BuO−, and π,π-stacking interaction between the substrate and the polymer backbone may account for the superior activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...