Metal organic framework-derived Co3O4 microcubes and their catalytic applications in CO oxidation
Abstract
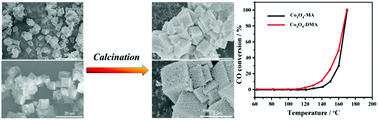
Metal–organic framework (MOFs)-derived metal oxides with diverse morphologies and microporous structures have shown potential applications in heterogeneous catalysis. In this study, two types of porous Co3O4 catalysts, Co3O4–MA and Co3O4–DMA (MA = methylamine and DMA = dimethylamine), were successfully synthesized via a one-step pyrolysis of Co-based metal-formate frameworks, [Amine][Co(HCOO)3] (Amine = methylamine, dimethylamine), in air. The obtained porous Co3O4 catalysts were systematically characterized by XRD, SEM, TEM, XPS, H2-TPR, and N2 adsorption–desorption analysis. The results show that the obtained porous Co3O4 catalysts are composed of nanoparticles and inherit the morphology from the precursor [Amine][Co(HCOO)3]. Co3O4–MA and Co3O4–DMA exhibit an excellent catalytic activity for CO oxidation, with both of them reaching a 100% CO conversion at 170 °C.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...