Rational design and optimization of selenophenes with basic side chains as novel potent selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) for breast cancer therapy†
Abstract
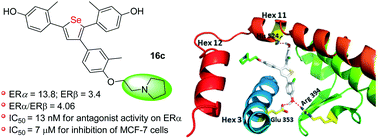
To increase the diversity of estrogen receptor (ER) ligands having novel structures and activities, series of selenophene derivatives with a basic side chain (BSC) were synthesized and their biological activity as subtype-selective antagonists for the ER was explored. Compared with the selenophenes without a BSC, most compounds showed an increase in binding affinity, and several compounds displayed enhanced antagonist potency and antiproliferative activity. Especially, compound 16c exhibited excellent transcriptional activity for ERα (IC50 = 13 nM) which made this compound the most potent antagonist for ERα of the whole series and is 66-fold better than the best selenophene compound without a BSC. Moreover, several compounds showed values of IC50 better than that of 4-hydroxytamoxifen in breast cancer MCF-7 cells. The modeling study indicated that the basic side chain might contribute to their increased antagonist potency and antiproliferative activity. These new ligands have the potential to be further developed as novel agents to improve therapeutics that target the estrogen receptor.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...