Abstract
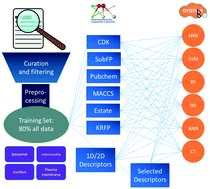
Chemical subcellular localization is closely related to drug distribution in the body and hence important in drug discovery and design. Although many in vivo and in vitro methods have been developed, in silico methods play key roles in the prediction of chemical subcellular localization due to their low costs and high performance. For that purpose, machine learning-based methods were developed here. At first, 614 unique compounds localized in the lysosome, mitochondria, nucleus and plasma membrane were collected from the literature. 80% of the compounds were used to build the models and the rest as the external validation set. Both fingerprints and molecular descriptors were used to describe the molecules, and six machine learning methods were applied to build the multi-classification models. The performance of the models was measured by 5-fold cross-validation and external validation. We further detected key substructures for each localization and analyzed potential structure–localization relationships, which could be very helpful for molecular design and modification. The key substructures can also be used as features complementary to fingerprints to improve the performance of the models.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...