Comparison of free-radical inhibiting antioxidant properties of carvedilol and its phenolic metabolites†‡
Abstract
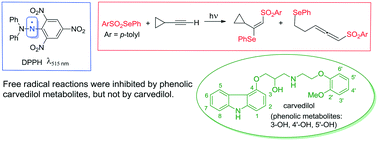
Carvedilol is a widely prescribed drug for the treatment of heart failure and the prevention of associated ventricular arrhythmias. It has also been reported to function as a biological antioxidant via hydrogen atom transfer from its carbazole N–H moiety to chain-propagating radicals. Metabolites of the drug include phenolic derivatives, such as 3-hydroxy-, 4′-hydroxy- and 5′-hydroxycarvedilol, which are also potential antioxidants. A comparison of the radical-inhibiting activities of the parent drug and the three metabolites was carried out in two separate assays. In the first, hydrogen atom transfer from these four compounds to the stable radical DPPH was measured by the decrease in the UV-visible absorption at 515 nm of the latter. The known radical inhibitors BHT, 4-hydroxycarbazole and α-tocopherol were employed as benchmarks in parallel experiments. In the second assay, inhibition of the photoinduced free-radical 1,2-addition of Se-phenyl p-tolueneselenosulfonate to cyclopropylacetylene, along with competing ring-opening of the cyclopropane ring, was monitored by 1H NMR spectroscopy in the presence of the carvedilol-based and benchmark antioxidants. In both assays, carvedilol displayed negligible antioxidant activity, while the three metabolites all proved superior radical inhibitors to BHT, with radical-quenching abilities in the order 3-hydroxy- > 5′-hydroxy > 4′-hydroxycarvedilol. Among the metabolites, 3-hydroxycarvedilol displayed even stronger activity in both assays than α-tocopherol, the best of the benchmark antioxidants. These results suggest that the radical-inhibiting antioxidant properties that have been attributed to carvedilol are largely or exclusively due to its metabolites and not to the parent drug itself.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...