Design, synthesis and cytotoxic activity of water-soluble quinones with dibromo-p-benzoquinone cores and amino oligo(ethylene glycol) side chains against MCF-7 breast cancer cells†
Abstract
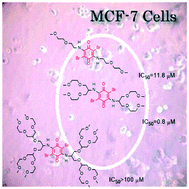
A series of novel quinones was synthesized by reacting tetrabromo-p-benzoquinone with amino oligo(ethylene glycol) dendrons of generation numbers g = 0–2. According to the performed shake-flask experiments, their aqueous solubility (S = 18 mg l−1–1.6 g ml−1) and partition coefficients (log Poct/wat = 2.53–0.21) can be tuned in a wide range as a function of g. In vitro cytotoxicity assays of tetrabromo-p-benzoquinone and its derivatives against MCF-7 human breast cancer cells showed a concentration- and generation-specific biological activity with IC50-values as low as 0.8 μM. Further investigations revealed a considerable selectivity against cancer cells, as indicated by a weak cytotoxicity against human skin fibroblast cells (>80% survival) within the studied range of concentrations. The results demonstrate that these novel amino oligo(ethylene glycol) dendrons depict versatile tools to ameliorate physical and pharmacological characteristics of extremely hydrophobic molecules and make them susceptible to biological applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...