Generation and characterization of the blood transcriptome of Macaca thibetana and comparative analysis with M. mulatta†
Abstract
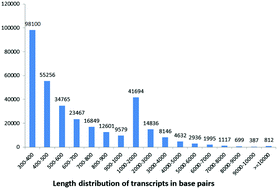
Transcriptome profiles provide a large transcript sequence data set for genomic study, particularly in organisms that have no accurate genome data published. The Tibetan macaque (Macaca thibetana) is commonly considered to be an endemic species to China and an important animal in biomedical research in the present day. In the present study, we report the de novo assembly and characterization of the blood transcriptome of the Tibetan macaque from three individuals, and we also sequenced the blood transcriptome of the rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta) for comparison. Using RNA-seq technology, 138 million sequencing reads of the M. thibetana transcriptome were generated. The assembly included 327 871 transcripts with an N50 of 1571 bp. According to the sequence similarity search, 80 317 (24.5%) transcripts were annotated in the nr protein database. All transcripts from M. thibetana and M. mulatta were functionally classified and compared using GO and KEGG analyses. The two transcriptomes were different in the GO term of nutrient reservoir activity, and in the KEGG subcategories of signaling molecules and interaction, infectious diseases, cell growth and death, and immune system. The transcriptomes in this study would provide a valuable resource for future functional and comparative genomic studies, and even for biological studies of this non-human primate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...