A portable multi-collector system based on an artificial optical compound eye for stand-off laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
Abstract
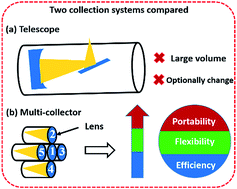
Stand-off laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (ST-LIBS) has attracted increasing attention as a valuable method for the remote analysis of materials. In this work, a multi-collector (MC) system combining low cost small lenses imitating the structure and shape of an artificial optical compound eye (AOCE) is presented to enhance the spectral intensity of ST-LIBS. The volume of the MC system is one eighteenth smaller than that of a telescope system and the number of collectors can be flexibly changed according to the requirements. The mechanisms of spectral enhancement are also discussed. In order to illustrate the performance of the MC system, the spectral intensities and the limits of detection (LoDs) of Mn and Cr elements acquired by the telescope system and the MC system were compared at a distance of 2 meters. The results showed that the spectral intensity acquired from the MC system was enhanced by 2.2 times, and the LoDs of Mn and Cr were decreased to 294 μg g−1 and 49 μg g−1. These results indicate that the MC system has great potential in providing a portable, flexible and effective collection method for remote detection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...