Contribution of single particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation for the characterization of silver nanosuspensions. Comparison with other sizing techniques†
Abstract
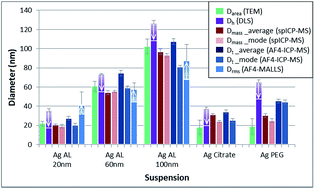
The determination of the size and size distribution of five silver nanocolloid populations has been assessed by different techniques. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was proposed as a reference in single particle methods. It was compared with three particle population methods: dynamic light scattering (DLS), very usual in particle population sizing, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in the single particle mode (spICP-MS), and asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation (AF4) coupled with multi-angle laser light-scattering detection (MALLS) and ICP-MS. These last two methods are gaining popularity because they provide a very complete description of the particle populations of interest, enabling access to both sizing and chemical composition. Depending on the polydispersity of the particle populations, some discrepancies did arise between the different techniques. It was found that local analysis performed by TEM tends to underestimate the mean diameter, while DLS almost always yields the largest estimate of the size. spICP-MS and AF4-MALLS-ICP-MS provided results which are consistent with the reference TEM and DLS methods in simple cases of monomodal, monodisperse populations. For less uniform distributions, for which DLS was not able to resolve the different modes, spICP-MS featured better resolution between the coexisting modes than AF4-MALLS-ICP-MS, but the latter allowed detection of smaller particles. For both techniques, care must be taken in the calibration steps: quantification of the particle mass in the case of spICP-MS and elution time for AF4-MALLS-ICP-MS. The analysis of silver colloids and the calibration with ionic standards could not be performed in the same matrix, leading to different ICP-MS signal sensitivities; introduction of recovery factors in the data processing was necessary for analytical result quality.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...