Micelle formation as a factor influencing the mode(s) of metal ion partitioning into N-alkylpyridinium-based ionic liquids (ILs): implications for the design of IL-based extraction systems†
Abstract
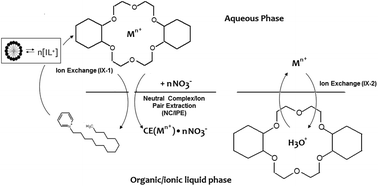
Prior studies of metal ion partitioning between an acidic aqueous phase and an ionic liquid in the presence of a macrocyclic polyether have demonstrated that the overall partitioning is a composite of three distinct pathways: neutral complex/ion-pair extraction, exchange of a cationic metal-crown ether (CE) complex for the cationic constituent of the IL, and exchange of the metal ion for a hydronium ion in a CE-H3O+ complex formed during acid preconditioning of the IL. The obvious undesirability of the ion-exchange pathways, which can lead to substantial loss of the IL cation to the aqueous phase, has led to efforts to identify means by which these processes can be suppressed or eliminated. Prior work with N,N′-dialkylimidazolium and quaternary ammonium bis [(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]imides has shown that increasing the hydrophobicity of the IL cation can be an effective means of diminishing the contribution of ion-exchange. Work with the corresponding N-alkylpyridinium ILs, however, indicates that in certain instances, an increase in the hydrophobicity of the IL cation is accompanied by a marked increase in its propensity to self-associate, leading to the formation of micelles in the aqueous phase. The net effect is to diminish or even negate the expected beneficial effect of IL cation hydrophobicity in reducing the contribution of ion exchange to the overall metal ion partitioning process, adversely impacting the “greenness” of extraction processes employing these ILs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...