UiO-66 derived Ru/ZrO2@C as a highly stable catalyst for hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone†
Abstract
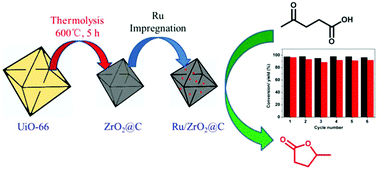
The hydrogenation of levulinic acid (LA) to γ-valerolactone (GVL) is a crucial reaction included in many biorefinery schemes for the production of renewable chemicals and fuels. The development of highly stable supported Ru-based catalysts in the polar protic liquid phase under hydrothermal conditions is still a major challenge. Here, we prepared a 0.85 wt% Ru/ZrO2@C catalyst using a new stabilization strategy based on the UiO-66 (Zr-MOF) material. The catalytic performance of this Ru/ZrO2@C in LA-to-GVL was tested and compared with commercial 5 wt% Ru/C at 10 bar H2, 413 K in water and also in high protic aqueous solution (pH = 1). The full conversion of LA and quantitative yield of GVL were achieved with both catalysts. However, the 5 wt% Ru/C showed poor resistance to deactivation already after the first run. ICP, XPS, HRTEM, AC-STEM, TPR and physisorption data showed that quick deactivation of Ru/C was mainly caused by the leaching of ruthenium in addition to the loss of surface area via carbonaceous deposition in micro-pores. In contrast, the self-prepared Ru/ZrO2@C catalyst showed no apparent drop in catalytic performance either in water or in high protic aqueous solution upon multiple recycling, and no leaching of ruthenium was found even under harsh conditions (pH = 1). Remarkably, in the Ru/ZrO2@C catalyst, Ru (probable single-atom) was highly dispersed on nanotetragonal ZrO2 (3.3 nm), embedded in the amorphous carbon, and no apparent Ru nanoclusters were observed even after reactions. TPR results indicated that this excellent stability might be attributed to strong metal–support interaction between Ru and nanotetragonal ZrO2.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...