Phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity, antiproliferative activity and bioaccessibility of Sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides L.) berries as affected by in vitro digestion†
Abstract
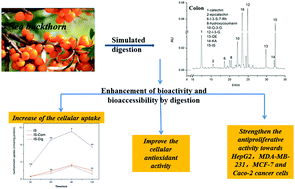
Phenolics, antioxidant and antiproliferative properties of Sea buckthorn berries were evaluated using a simulated in vitro digestion and compared with a chemical extraction method. Digested samples were subjected to antiproliferation evaluation against human liver, breast and colon cancer cells. Furthermore, the bioaccessibility of digested berries was evaluated using a Caco-2 cell culture model. Results revealed that after enzymatic digestion the phenolic compounds were quite different from the chemical extracts, more flavonoid aglycones were released, whereas less total phenolics, phenolic acids and flavonoid glycosides were detected. Although the extracellular antioxidant activity of the digesta was lower than that of extracts, the cellular antioxidant activity (CAA) and antiproliferative effects of berries were significantly enhanced by digestion. This was attributed to their higher flavonoid aglycone content and could be verified by testing individual active compounds, suggesting that the cellular uptake of samples might be improved, which was also certified by the Caco-2 cell uptake model. The digested samples showed an almost 5-fold cellular accumulative amount of isorhamnetin than pure isorhamnetin, which was attributed to the significant down regulation of the mRNA expression level of efflux transporters MRP2 and P-gp. This finding indicated that the digestion enhanced the bioaccessibility of bioactive compounds of berries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...