Antioxidant, ACE-inhibitory and antimicrobial activity of fermented goat milk: activity and physicochemical property relationship of the peptide components
Abstract
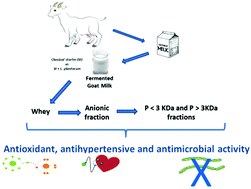
Increasing evidence on goat milk and the health benefits of its derived products beyond its nutritional value show its potential as a functional food. In this study, goat milk fractions were tested for their total antioxidant capacity using different methods (ORAC, ABTS, DPPH and FRAP), as well as their angiotensin-I-converting-enzyme inhibitory and antimicrobial (against Escherichia coli and Micrococcus luteus) activities. Different whey fractions (whey, cation exchange membrane permeate P and retentate R) of two fermented skimmed goat milks (ultrafiltered goat milk fermented with the classical starter bacteria or with the classical starter plus the Lactobacillus plantarum C4 probiotic strain) were assessed. Additionally, P fractions were divided into two sub-fractions after being passed through a 3 kDa cut-off membrane: (a) the permeate with peptides of MW <3 kDa (P < 3); and (b) the retentate with peptides and proteins of MW >3 kDa (P > 3). No differences in biological activities were observed between the two fermented milks. However, the biological peptides present in the P < 3 fraction showed the highest total antioxidant capacity (for the ORAC assay) and angiotensin-I-converting-enzyme inhibitory activity. Those present in the R fraction showed the highest total antioxidant capacity against ABTS˙+ and DPPH˙ radicals. Some antimicrobial activity against E. coli was observed for the fermented milk containing the probiotic, which could be due to some peptides being released by the probiotic strain. In conclusion, small and non-basic bioactive peptides could be responsible for most of the angiotensin-I-converting-enzyme inhibitory and antioxidant activities. These findings reinforce the potential benefits of the consumption of fermented goat milk in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases associated with oxidative stress and hypertension.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...