Cellular antioxidant, methylglyoxal trapping, and anti-inflammatory activities of cocoa tea (Camellia ptilophylla Chang)
Abstract
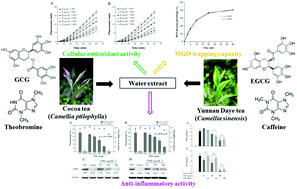
Cocoa tea (Camellia ptilophylla Chang) is a naturally low caffeine-containing but gallocatechin gallate (GCG)-rich tea cultivar, though its biological activities have not been extensively explored. Herein, we evaluated the in vitro cellular antioxidant, methylglyoxal trapping, and anti-inflammatory activities of water extract of green tea from cocoa tea (CWE) and Yunnan Daye tea (Camellia sinensis) (YWE), and their predominant bioactive components GCG and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) for comparative purposes. Primarily, CWE exhibited a higher cellular antioxidant potential than YWE via a cellular antioxidant activity assay, while no significant difference was observed between GCG and EGCG. Moreover, CWE was more potent than YWE in the inhibitory effect on inflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages, including nitric oxide and interleukin-6 productions. Additionally, CWE showed comparable MGO trapping ability to YWE, although EGCG was more reactive with MGO than with GCG. This study suggested that cocoa tea would be a promising and potential functional beverage as a dietary antioxidant, methylglyoxal trapping, and anti-inflammatory agent.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...