Molecular adaptations underlying the beneficial effects of hydroxytyrosol in the pathogenic alterations induced by a high-fat diet in mouse liver: PPAR-α and Nrf2 activation, and NF-κB down-regulation†
Abstract
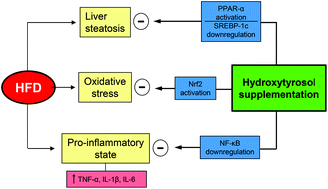
Scope: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition characterized by an increment in the liver fat content, with a concomitant reduction in the content of n-3-long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 LCPUFAs), downregulation of PPAR-α activity, and upregulation of NF-κB activity, effects that induce pro-lipogenic and pro-inflammatory responses. Hydroxytyrosol (HT), a polyphenol with cytoprotective effects present in extra virgin olive oil, improves the cellular antioxidant capacity for activation of transcription factor Nrf2. The objective of this work is to evaluate the molecular adaptations involved in the anti-lipogenic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-oxidant effects of HT supplementation in high-fat diet (HFD)-fed mice. Methods and results: Male C57BL/6J mice received (i) control diet (10% fat); (ii) control diet + HT (daily doses of 5 mg per kg body weight), (iii) HFD (60% fat); or (iv) HFD + HT for 12 weeks. HFD-fed mice exhibited (i) liver steatosis; (ii) inflammation; (iii) oxidative stress; and (iv) depletion of n-3 LCPUFAs, together with down-regulation of PPAR-α and Nrf2, and up-regulation of NF-κB. HT supplementation attenuated the metabolic alterations produced by HFD, normalizing the activity of Nrf2, reducing the drop in activity of PPAR-α, and attenuating increment of NF-κB activation. Conclusion: Supplementation with HT activating transcription factors PPAR-α and Nrf2, along with the deactivation of NF-κB, may reduce the liver alterations induced in HFD-fed mice.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...