Cementitious materials modified with hematite nanoparticles for enhanced cement hydration and uranium immobilization
Abstract
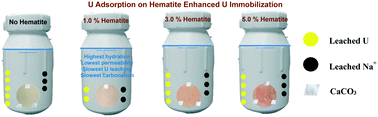
The leakage of low and intermediate level radioactive wastes from cementitious barriers at disposal sites can pose long-term environmental threats. In this study, cementitious materials were modified with hematite nanoparticles at 1.0%, 3.0%, and 5.0% by mass to enhance uranium immobilization for the first time. After curing the specimens for 28 days, leaching experiments were carried out at 90 °C up to 28 days. The leached uranium and sodium ions in solutions were quantified, and the effects of hematite nanoparticles on the physicochemical and mechanical properties of cementitious materials were studied. The experimental results revealed that the addition of 1.0%, 3.0% and 5.0% hematite nanoparticles all significantly reduced uranium leaching, which is partially due to uranium adsorption onto hematite nanoparticles. Interestingly, the slowest uranium leaching was found in the specimens with 1.0% hematite nanoparticles. The leaching results were complemented by isothermal calorimetry measurements, mercury intrusion porosimetry, chemical analysis, and compression tests, which showed that hematite nanoparticles increased the cement hydration rate and degree, affected cementitious material pore structure development, decreased leachability, and increased compressive strength. These effects were found to be the strongest in specimens containing 1.0% hematite nanoparticles. This study provides new insights into the modification of cementitious materials with hematite nanoparticles for enhanced cement hydration and uranium immobilization. It suggests an economical strategy for the long-term disposal of low and intermediate level radioactive wastes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...