Activation of antioxidant and detoxification gene expression in cucumber plants exposed to a Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide†
Abstract
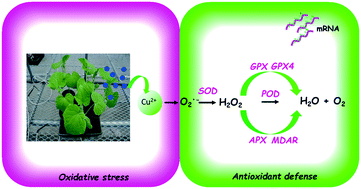
Cu-containing nanopesticides are increasingly being used as fungicides in modern agriculture. However, their fate, transport and toxicity in crop plants have been less studied. Here, we exposed 3 week-old cucumber plants cultivated in artificial media to different concentrations of a Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide (0, 2.5 and 25 mg) for 7 d. The physiological and molecular responses were investigated. In order to elucidate the contribution of copper ions to the response, we also exposed the plants to CuSO4. Results showed that the Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide did not reduce the photosynthetic pigment production. In contrast, 10 mg Cu ions induced a significant decrease in photosynthetic pigment levels (around 25%) and leaf chlorosis symptoms. Foliar exposure to 25 mg Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide induced significant changes in mRNA levels of antioxidant and detoxification-related genes; 6 genes (SOD, GPX4, GPX, MDAR, POD, WRKY6) were up-regulated up to 9-fold, and one (cAPX) was down-regulated by 32%. The Cu(OH)2 nanopesticide at both dose levels (2.5 and 25 mg per plant) decreased the transcript production of a stress-related gene (DNAJ) by 40% and 80%, respectively. The up-regulation of the transcript levels of SOD, GPX4, GPX, MDAR, POD, and WRKY6 and down-regulation of DNAJ was also observed in CuSO4 treated plants (with increases of up to 7-fold), indicating that most of the responses are due to released copper ions. We postulate that the increased mRNA levels of antioxidants and detoxification enzymes reflect plant adaptation to over-generated reactive oxygen species (ROS) triggered by copper ions. The activated genes could serve as potential biomarkers of nanopesticide exposure and may be applicable to other plant/Cu nanopesticide interactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...