Morphology, structure, and metal binding mechanisms of biogenic manganese oxides in a superfund site treatment system†
Abstract
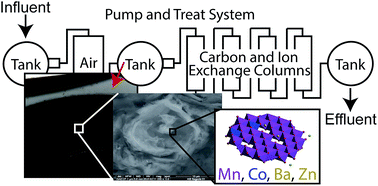
Manganese oxides, which may be biogenically produced in both pristine and contaminated environments, have a large affinity for many trace metals. In this study, water and Mn oxide-bearing biofilm samples were collected from the components of a pump and treat remediation system at a superfund site. To better understand the factors leading to their formation and their effects on potentially toxic metal fate, we conducted a chemical, microscopic, and spectroscopic characterization of these biofilm samples. Scanning electron microscopy revealed the presence of Mn oxides in close association with biological structures with morphologies consistent with fungi. X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) revealed the oxides to be a mixture of layer and tunnel structure Mn(IV) oxides. In addition, XAS suggested that Ba, Co, and Zn all primarily bind to oxides in the biofilm in a manner that is analogous to synthetic or laboratory grown bacteriogenic Mn oxides. The results indicate that Mn oxides produced by organisms in the system may effectively scavenge metals, thus highlighting the potential utility of these organisms in designed remediation systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...