The electrochemical effect of various Si/Zr molar ratios on anode materials in lithium-ion batteries
Abstract
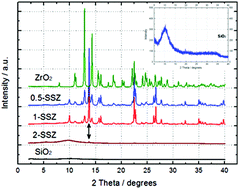
The aim of this study was to unveil the mechanisms of SiO2/ZrO2 (SSZ) anode materials through electrochemical analysis and to understand the effect of various Si/Zr molar ratios (Si/Zr = 0.5, 1, and 2) on the performance of SSZ anode materials with these mechanisms. The 2-SSZ (Si/Zr = 2) electrode had a much higher capacity than that of the 0.5- or 1-SSZ (Si/Zr = 0.5 or 1) electrode. It exhibited superior cycling performance when compared to commercial graphite (theoretical capacity of 372 mA h g−1). The 2-SSZ had a capacity of 461 mA h g−1 at a high current density of 100 mA g−1 over 30 cycles. These characteristics are due to the effects from each of the different reversible materials formed by the SSZs. Zr2Si and Zr5Si3, ZrSi, or ZrSi2 were formed by the 0.5-, 1-, and 2-SSZs, respectively, which would affect the reversible storage capacity. ZrSi2 provided an increase in the possible reaction area for the guest species (lithium ions) at the empty interstitial site in the host materials as well as a large area for accommodating a volume change. It was supportive by maintaining the lattice constant and reducing the ratio of the structure distortion. Furthermore, the 2-SSZ structure consisted of an overall amorphous structure with a crystalline structure related to the Zr–O–Si bond unlike the 0.5- and 1-SSZs which had an overall crystalline structure. Such a combined structure of 2-SSZ was advantageous for providing good capacity due to the amorphous structure and an efficient pathway for electron transport and little pulverization due to the crystalline structure. This structure led to its superior performance and long lifespan.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...