Bifunctional colorimetric chemosensing of fluoride and cyanide ions by nickel-POCOP pincer receptors†
Abstract
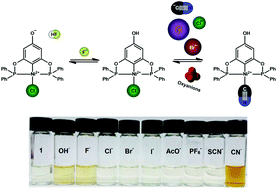
Three Ni(II)-POCOP pincer complexes [NiCl{C6H2-4-OH-2,6-(OPPh2)2}], 1; [NiCl{C6H2-4-OH-2,6-(OPtBu2)2}], 2 and [NiCl{C6H2-4-OH-2,6-(OPiPr2)2}], 3 were studied as bifunctional molecular sensors for inorganic anions and acetate. In CH3CN, fluoride generates a bathochromic shift with a colorimetric change for 1–3 with a simultaneous fluorescence turn on, this optical effect is based on deprotonation of the para-hydroxy group of the POCOP ligand. On the other hand, in a neutral aqueous solution of 80 vol% CH3CN, additions of cyanide produce a distinct change of color by forming very stable complexes with the nickel-based receptors 1–3 with log Ka in the range of 4.38–5.03 M−1 and pronounced selectivity over other common anions such as iodide, phosphate, and acetate. Additionally, bromide shows a modest spectral change and affinity, but lower than those observed for cyanide. On the basis of 1H NMR experiments, UV-vis titrations, ESI-MS experiments, and the crystal structure of the neutral bromo complex of 1, it is proposed that the colorimetric change involves an exchange of chloride by CN− on the Ni(II) atom. The Ni(II)-based sensor 1 allows the fluorescent selective detection of fluoride with a limit of 5.66 μmol L−1 and colorimetric sensing of cyanide in aqueous medium in the micromolar concentration range.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...