Copper-promoted methylene C–H oxidation to a ketone derivative by O2†
Abstract
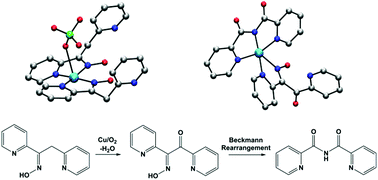
The methylene group of the ligand 1,2-di(pyridin-2-yl)-ethanone oxime (dpeo) is slowly oxygenated by the O2 in air under ambient conditions when [Cu(dpeo)2](ClO4)2 is dissolved in ethanol or acetonitrile. An initial transient ketone product, 2-(hydroxyimino)-1,2-di(pyridine-2-yl)ethanone, (hidpe) was characterized in the heteroleptic copper(II) complex [Cu(bpca)(hidpe)](ClO4). The co-ligand in this complex, N-(2′-pyridylcarbonyl)pyridine-2-carboximidate (bpca−), is derived from a copper-promoted Beckmann rearrangement of hidpe. In the presence of bromide only [Cu(bpca)Br] is isolated. When significant water is present in reaction mixtures copper complexes of dpeo, hidpe and bpca− are not recovered and [Cu(pic)2H2O] is isolated. This occurs since two equivalents of picolinate are ultimately generated from one equivalent of oxidized and hydrolysed dpeo. The copper-dependent O2 activation and consequent stoichiometric dpeo C–H oxidation is reminiscent of the previously observed catalysis of dpeo oxidation by Mn(II) [C. Deville, S. K. Padamati, J. Sundberg, V. McKee, W. R. Browne, C. J. McKenzie, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 545–549]. By contrast dpeo oxidation is not observed during complexation reactions with other late transition metal(II) ions (M = Fe, Co, Ni, Zn) under aerobic conditions. In these cases bis and tris complexes of bidentate dpeo are isolated in good yields. It is interesting to note that dpeo is not oxidised by H2O2 in the absence of Cu or Mn, suggesting that metal-based oxidants capable of C–H activation are produced from the dpeo-Cu/Mn systems and specifically O2. The metastable copper complexes [Cu(dpeo)2](ClO4)2 and [Cu(bpca)(hidpe)](ClO4), along with [NiX2(dpeo)2] (X = Cl, Br), [Ni(dpeo)3](ClO4)2, [Co(dpeo)3](ClO4)3 and the mixed valence complex [FeIIIFeII2(dpeo-H)3(dpeo)3](PF6)4, have been structurally characterized.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...